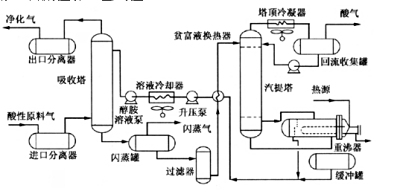
A typical process for amine desulphurisation and decarburisation consists of four parts: absorption, flash evaporation, heat exchange and regeneration (stripping).
Variable Pressure Adsorption (VPA) CO2 removal process is widely used in ammonia, methanol, butanol decarbonisation units and urea, soda ash, industrial CO2 purification CO2 units as well as chi gas and CO2-containing tail gas recovery units due to its high degree of automation, convenient adjustment of removal accuracy, wide range of application, low energy consumption, and other features.
Pressure-variable adsorption nitrogen generator (PSA nitrogen generator for short) is a nitrogen generating equipment designed and manufactured according to pressure-variable adsorption technology.
Wet decarbonisation is a widely used decarbonisation process with low energy consumption and is widely used to remove CO2 and H2S from ammonia, methanol feedstock gas, refinery gas, city gas and natural.
Hydrogen from light hydrocarbon water vapour reforming is also a relatively traditional technology, and was previously commonly used for large-scale hydrogen supply, e.g. above 5000 m3/h.
This process uses methanol and demineralised water from convenient sources as raw materials, which are catalytically converted over a specialised catalyst at 220-280°C into a reformed gas containing mainly hydrogen and carbon dioxide.
Purification of carbon monoxide from mixtures containing carbon monoxide, hydrogen, nitrogen, methane, carbon dioxide and other components using the variable pressure adsorption process.
The company's proprietary technology developed for low concentration gas, after fully analysing the nature of the raw gas, adopts variable pressure adsorption under micro-pressure conditions to separate CH4 and N2/O2.
To produce LNG from natural gas, the CO2, H2S and other components in natural gas are firstly absorbed by MDEA solution, and the unabsorbed purified gas is dried after liquid separation and then put into the cold box to produce LNG.
PSA method of biogas concentration is to use adsorbent to separate methane, carbon dioxide and nitrogen in biogas, so as to achieve the purpose of methane concentration.
Oil tanks, loading emission gas, petrochemical and chemical production of VOC-containing tailpipe gas, the first variable pressure adsorption concentration, and then condensation recovery process, so as to meet the requirements of environmental protection emissions, but also to recover part of the organic matter.
In industrial hydrogen purification by pressure swing adsorption (PSA), the adsorbents generally adsorb the easily adsorbed components out of the gas mixture at ambient temperature and high pressure, while the not easily adsorbed components (such as hydrogen) flow out from one end of the bed as the product
Because blast furnace gas contains organic sulphur, H2S and other impurities, using blast furnace gas etc. as fuel, SO2 in the flue gas cannot reach the emission standard. There are two main measures for emission reduction: desulphurisation of blast furnace gas or flue gas desulphurisation at the end.