VOCs exhaust treatment 9 processes, scope of application and cost control
With the increasing industrialisation, the pollution of VOCs has a tendency to expand further. And with the recent environmental protection policies become more and more stringent, the emission control of organic pollution waste gas becomes more important. Here we take a look at what technologies are available at home and abroad? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each?
With the increasing industrialisation, the pollution of VOCs has a tendency to expand further. And with the recent tougher environmental protection policies, the control of emissions of organic pollutants becomes even more important. Here we take a look at what technologies are available at home and abroad? What are the advantages and disadvantages?
First, the principle of treatment and classification

The current treatment of volatile organic pollutants, including destructive, non-destructive methods, and a combination of these two methods.
Destructive methods include combustion, biological oxidation, thermal oxidation, photocatalytic oxidation, low-temperature plasma and its integrated technology, mainly by chemical or biochemical reactions, light, heat, microorganisms and catalysts will be converted into VOCs CO₂ and H₂O and other non-toxic inorganic small molecular compounds.
Non-destructive methods, i.e. recycling methods, are mainly carbon adsorption, absorption, condensation and membrane separation technologies, which enrich and separate volatile organic compounds by physical methods, controlling temperature, pressure or with selective permeation membranes and selective adsorbents.
Traditional volatile waste gas treatment commonly used absorption, adsorption removal, combustion removal, etc. In recent years, the semiconductor photocatalyst technology body, low-temperature plasma has been rapidly developed.
Second, the treatment process analysis
1、Adsorption process
(1) Introduction to adsorption process
Adsorption method is mainly applicable to the purification of low concentration of gaseous pollutants, for the high concentration of organic gases, usually need to be condensed first to reduce the concentration of such processes and then adsorption purification. Adsorption technology is the most classic and commonly used gas purification technology, and is also one of the mainstream technologies for industrial VOCs treatment. The key technologies of adsorption method are adsorbent, adsorption equipment and process, regeneration medium, post-treatment process and so on.
Activated carbon is widely used in the adsorption and recovery of organic gases because of its large specific surface area and microporous structure. At present, the research on the adsorption of organic gases by activated carbon mainly focuses on the prediction of adsorption equilibrium, the modification of activated carbon materials and the influence of the physical and chemical properties of organic substances on the adsorption performance of activated carbon.
(2) Principle and flow of activated carbon adsorption process

Activated carbon fibre adsorption of organic waste gas is one of the most advanced technologies in the world today, activated carbon fibre has a larger adsorption capacity and faster adsorption kinetic performance than granular activated carbon, activated carbon adsorption, desorption process is shown in Figure 1.
(3) Activated carbon adsorption process influencing factors

(4) Physical adsorption of activated carbon for air purification, as shown in four cases in Figure 2:
- The molecular diameter is greater than the diameter of the pore, due to spatial site resistance, the molecules can not enter the pore, so no adsorption;
- The molecular diameter is equal to the diameter of the pore, and the adsorbent has a strong trapping power, making it ideal for low concentration adsorption;
- The molecular diameter is smaller than the pore diameter, capillary condensation occurs in the pore, and the adsorption capacity is large;
- The molecular diameter is much smaller than the diameter of the hole, the adsorbed molecules are easily desorbed, the desorption rate is high, and the adsorption capacity at low concentration is small.
(5) Advantages and disadvantages of activated carbon adsorption process
Advantages:
- Applicable to low concentration of various pollutants;
- The price of activated carbon is not high, and energy consumption is low, so it is more economical to apply;
- Solvent organics can be recovered through desorption and condensation;
- Easy to apply, only in contact with air;
- Activated carbon has good acid and alkali resistance and heat resistance, high chemical stability.
Disadvantages:
- Small adsorption capacity, there is adsorption saturation problem in physical adsorption, as the adsorbent is consumed, the adsorption capacity becomes weaker, and small adsorption capacity or loss of adsorption function may occur after a period of use;
- When adsorption, there is a problem of adsorption specificity, for mixed gases, the adsorption may be weakened, and there is also a mismatch between the molecular diameter and the pore size of the activated carbon, resulting in the phenomenon of desorption;
2、Absorption process
(1) Introduction to the absorption process
The method of absorbing volatile gases in industrial waste gas with solution, solvent or water to separate them from the waste gas is called absorption method. The solution, solvent and water are called absorbents. Different absorbents can absorb different harmful gases.
The absorption equipment used in the absorption method is called absorber, purifier or scrubber. Absorption process and wet dust removal process is similar, just wet dust removal process with water, while the absorption method to purify harmful gases with solvents or solutions.
(2) Absorption process principle and flow

Taking oil and gas recovery as an example, oil and gas recovery should include refineries, chemical plants, oil and gas stations loading, unloading, and generating oil and gas. Oil and gas from the plant to the sales terminal is a complete system.
The United States and European countries, usually in the petrol station using one-stage and two-stage oil and gas recovery measures, that is, closed unloading and refuelling, tank oil and gas returned to the tanker trucks, the use of vacuum assisted devices or tank pressure during refuelling to return to the storage tanks. Oil and gas recovery devices are installed at oil depots, refineries and other petroleum product distribution sites to recover oil and gas.
Absorption methods are commonly used for oil and gas recovery. Loading and unloading of oil produced when the oil and gas into the absorption tower, from the exit of the oil-poor air, desorption tower for the vacuum desorption of the absorbing liquid, desorption of the absorbing liquid recycling, recycling tower with gasoline will enter the desorption of gas recovery, the tail gas back to the absorption tower to repeat the process. Recovery of volatile organic compounds with solution absorption method of the absorption liquid is usually a special absorption liquid, the choice of the absorption liquid will affect the recovery effect.
(3) Absorption process advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:Absorption process is relatively simple, low investment in equipment, operation and maintenance costs are basically comparable to the carbon adsorption method, because the absorption medium is used paraffin and absorption liquid, so there is no secondary pollution problems.
Disadvantages:This process method recovery efficiency is low, for environmental protection requirements are high, it is difficult to meet the permissible oil and gas emission standards; equipment occupies a large space; high energy consumption; absorbent consumption is large, need to be constantly replenished.
3、Condensation process
(1) Introduction to condensation process
Some light hydrocarbon components volatilise into the atmosphere during the storage, transportation and sale of oil products, causing waste of resources and environmental hazards. At the same time, organic solvents are widely used in industrial production, every year a large number of organic solvents volatilised into the air, endangering human health and causing serious environmental pollution. Adopting suitable methods to recover these VOCs not only reduces the production cost of enterprises, but also has great environmental benefits.
Condensation method is used to recover VOCs an effective method, the basic principle is to use the gaseous pollutants at different temperatures and pressures have different saturated vapour pressure, by lowering the temperature and increasing the pressure, so that some of the organic matter condensed out, so that the VOCs can be cleaned up and recovered.
(2) Condensation process principle and flow

Condensing oil and gas recovery equipment adopts multi-stage compounding or self-compounding refrigeration technology, and although the system process is relatively complex, its key components, compressor and throttling mechanism have all been realised in localised production, with low investment and operating costs.
According to the working principle of heat exchanger tube can be divided into refrigerant circuit and gas circuit part, heat exchanger tube connects the two parts. In the gas circuit part, low-temperature refrigerant in the heat exchanger and hot organic solvent mixture for heat exchange, organic solvent liquefaction and recovery, the refrigerant flows into the liquid storage tank.
Refrigerant circuit, the compressor compresses the refrigerant into a high-temperature, high-pressure gaseous refrigerant, liquefied through the air-cooled condenser, through the filter drier, in the refrigerant-refrigerant heat exchanger in the cold liquid refrigerant and refrigerant heat exchange, low-temperature refrigerant into the reservoir, refrigerant through the inhalation filter into the compressor inlet, to complete the entire refrigerant refrigerant heat exchange process.
(3) Influence factors of condensation process
Condensation separation method to recover light hydrocarbons to cool the raw gas cooling. According to the principle can be divided into throttling expansion refrigeration, expander expansion refrigeration. According to the process can be divided into refrigerant refrigeration (such as propane refrigeration), throttling expansion refrigeration, expansion refrigeration, mixed refrigeration (in the expansion refrigeration or process fluid itself throttling expansion refrigeration on the basis of external refrigerant refrigeration).
Separation methods include distillation separation in distillation systems and phase equilibrium separation in separators. The process generally includes dehydration, pressurisation (low pressure gas), distillation and refrigeration. The selection of each part of the above condensation process affects the final condensation effect.
(4) Advantages and disadvantages of the condensation process
Advantages:
Condensation method is the use of material boiling point of different recovery, suitable for higher boiling point of organic matter, the method has the recovery of high purity, equipment and process is simple, the advantages of low energy consumption; and compact equipment, occupies a small space, a high degree of automation, easy maintenance, safety, the output of liquid oil can be directly used and other advantages;
Disadvantages:
Single condensation method to meet the standard needs to be reduced to a very low temperature, huge power consumption, not the true meaning of "energy saving".
4, membrane separation process
(1) membrane separation process
In the process of oil extraction and storage and transport, part of the oil volatilised to the atmosphere in the formation of oil and gas, in addition to air, the main C4-C5 and a small amount of aromatic hydrocarbons. These organic vapour emissions not only cause a serious waste of resources, but also have a great impact on air quality, and thus affect human health, at present, the separation and recovery of organic vapour methods are mainly condensation, activated carbon adsorption, membrane separation method, solvent absorption method. Membrane separation technology is a more efficient separation method .
(2) Membrane separation process principles and procedures
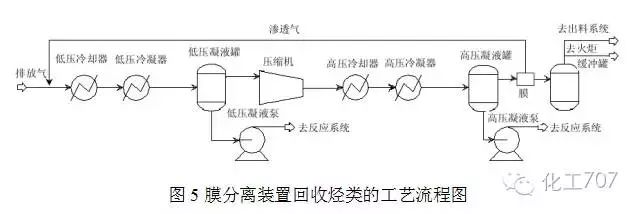
Membrane Separation Organic Vapour Recovery System achieves separation through the dissolution-diffusion mechanism. Gas molecules in contact with the membrane, dissolved on the surface of the membrane, and then on the surface of both sides of the membrane will produce a concentration gradient, because different gas molecules through the dense membrane dissolution diffusion speed is different, so that the gas molecules by the membrane to the other side of the membrane diffusion, and finally from the other side of the surface of the membrane desorption, and ultimately achieve the purpose of separation.
Membrane separation device is set up after the high-pressure condenser, before the buffer tank, due to the discharge of gas compressor capacity is insufficient, only a part of the gas through the membrane separation device, the other part of the direct access to the buffer tank, permeate the gas back to the low-pressure cooler before the tail gas into the buffer tank.
(3) Influence factors of membrane separation process
The material of the support layer has an important influence on the permeation rate and hydrocarbon VOCs recovery rate, for the same material of the support layer, the permeation rate and hydrocarbon VOCs recovery rate increases with the decrease of pore diameter, but when the pore diameter is reduced to a certain critical value, with the pore diameter continues to decrease, the permeation rate and the hydrocarbon VOCs recovery rate will decrease.
(4) Membrane separation process advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
Membrane separation technology is the cutting-edge technology of separation science in modern petrochemical disciplines. It has the characteristics of small investment, quick results, simple process, high recovery rate, low energy consumption, no secondary pollution, with high scientific and technological content;
Disadvantages:
Large investment; membrane domestic rate is low, expensive, and short membrane life; membrane separation device requires stable flow, stable pressure gas, high operational requirements.
5, combustion process
(1) combustion process
A class of VOCs treatment method is the so-called destructive technology, that is, through chemical or biological technology to make VOCs into carbon dioxide, water and hydrogen chloride and other non-toxic or toxic inorganic substances. Combustion is one such technology.
The combustion method is divided into direct combustion method and catalytic combustion method. Direct combustion method is suitable for the treatment of high concentrations of VOCs in the exhaust gas, because of its operating temperature is usually in the 800-1200 ℃, process energy costs are high, and combustion of exhaust gas is prone to dioxin, NOx and other by-products; due to the general low concentration of VOCs in the exhaust gas, relying only on the reaction heat, it is generally difficult to maintain the temperature required for the reaction.
In order to improve the thermal economy, a lot of research has been carried out, one direction is to improve the performance of catalysts to make the reaction temperature lower. Another direction is to study the new process technology, new reactor design in order to make the reaction can be achieved at a higher temperature of self-heating.
(2) Combustion process principle and flow

In catalytic combustion, preheating is a basic form of process. The organic waste gas is heated in the preheating chamber before entering the reactor, because the organic waste gas temperature is lower than 100 degrees Celsius, the concentration is low and the heat is not self-sufficient. After combustion and purification, the heat is exchanged with the untreated waste gas to recover some of the heat. Gas or electric heating is a common method for this process, heating to the ignition temperature required for the catalytic reaction.
(3) Influencing factors of combustion process
The choice of catalytic combustion catalyst is the key, and its performance plays a decisive role in eliminating efficiency and energy consumption. For VOC oxidation catalysts can generally be divided into 2 categories: precious metal catalysts (platinum, palladium, etc.) and metal oxide catalysts (copper, chromium, manganese, etc.), the precious metal catalysts are widely used in the catalytic combustion of volatile organic compounds because of their good ignition activity. Among the noble metal catalysts used for catalytic oxidation of VOCs, platinum is more active than palladium.
(4) Combustion process advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
Compared with the direct combustion method its auxiliary fuel costs are low, the generation of secondary pollutants NOx is low, the volume of the combustion equipment is small, and the VOCs removal rate is high;
Disadvantages:
The catalyst is more expensive, and the requirements of the exhaust gas must not contain components that will lead to catalyst deactivation.
6, biological filtration process
(1) Introduction to biological filtration process
The use of microbial metabolic processes on a variety of organic and some inorganic biodegradation, can effectively remove pollutants in the industrial waste gas, this is the treatment of organic waste gas biological method.
The first to propose the use of microorganisms to treat the concept of waste gas is Bach, he was in 1923 the use of soil filter beds to treat sewage treatment plants emitting odorous gases containing H2S. In many areas of Germany and the Netherlands, this technology has been applied on a large scale and successfully to control odours, volatile organic compounds and airborne toxic emissions, and the control efficiency of many common air pollutants has reached more than 90%.
(2) Biofiltration Process Principles and Procedures

The biofiltration process system consists of three parts: the gas conveying device, the spraying device and the main body of the filter tower. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are pre-wetted under pressure and come into contact with the biofilm on the surface of the packing layer in the filter tower. The VOCs are transferred from the gas phase to the biofilm, where they are decomposed by the microorganisms and utilised as carbon dioxide, water and other molecules, and the purified gases are then discharged. The spraying device regularly sprays the packing layer with spray liquid to regulate the moisture content, pH value and nutrient salt content of the packing layer.
(3) Influencing factors of the biofiltration process
Packing: In the biological droplet filter, biofilm grows on the surface of the packing, and gaseous organic matter flows through the gaps between the packing. Specific surface area of the size of the filler to a certain extent reflects the number of microorganisms, porosity affects the gas, liquid flow rate, and the height of the filler layer of organic matter whether the treatment is complete has an important significance.
Nutrient solution: Nutrients, trace elements and buffer solution are evenly sprayed on the packing to provide the nutrients required for the growth and reproduction of biological flora in the biofilm. The VOC removal rate is somewhat influenced by the flow rate of the nutrient solution, the nitrogen and phosphorus content, etc.
Inlet gas: during the operation of the biological droplet filter, the gas flow rate, the size of the inlet gas concentration have a significant impact on the removal efficiency of the gas itself.
(4) Advantages and disadvantages of the biofiltration process
Advantages:
Wide range of application, high processing efficiency, simple process, low cost, no secondary pollution .
Disadvantages:
The removal rate of VOCs with high concentration, poor biodegradability and difficult biodegradability is low.
7、Plasma process
(1) Introduction of plasma process
Plasma pollutant control technology uses gas discharge to produce highly reactive particles to react with a variety of organic and inorganic pollutants, so that the pollutant molecules are decomposed into small molecular compounds or oxidised into compounds that can be easily treated and removed.
The most important feature of this technology is that it can efficiently and conveniently destroy and decompose a variety of pollutants, using simple equipment, occupying less space and suitable for a variety of working environments.
(2) Plasma Process Principles and Procedures
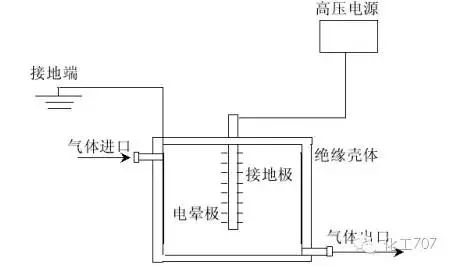
The main degradation mechanism of corona discharge, which is used to treat volatile organic compounds, is as follows: under the applied electric field, the electrons in the electrode space gain energy and begin to accelerate. The electrons in the process of movement and gas molecules collide with each other, so that the gas molecules are excited, ionised or adsorbed electrons become negative ions.
(3) Influence factors of plasma process
In the degradation process, the selection and control of the electrode voltage is its main content, which will affect the discharge of the discharge medium and the electron carrying energy, as well as a series of subsequent reactions, which in turn affects the degradation efficiency; at the same time, the electrode voltage also serves as an important parameter for the method to reach the commercial application, so the selection of the electrode voltage is particularly critical.
In addition to the close relationship between low temperature plasma degradation of VOCs and electrode voltage, it is also affected by the reactor structure, reaction background atmosphere, water content in the VOCs exhaust gas, discharge frequency, discharge voltage, chemical structure of VOCs, catalyst type, low-temperature plasma discharge form, reaction temperature, and the initial concentration of VOCs, etc., which is dominated by the influence of gas concentration and gas flow.
(4) Advantages and disadvantages of plasma process
Advantages:
High processing efficiency, low operating costs, especially for the removal of aromatic hydrocarbons with high efficiency.
Disadvantages:
For high concentrations of VOCs processing efficiency is general, currently mainly in the laboratory stage, the lack of practical applications.
8、Photocatalytic oxidation process
(1) Introduction of photocatalytic oxidation process
Photochemical and photocatalytic oxidation is a kind of advanced oxidation technology with more research at present. Photocatalytic reaction is the chemical reaction carried out under the action of light. After molecules absorb electromagnetic radiation of specific wavelengths, it is the molecules that reach the excited state, and then a chemical reaction occurs to produce new substances or become the initiator of thermal reactions.
(2) Principle and flow of photocatalytic oxidation process

Ti02 as a semiconductor material has its own photovoltaic properties that determine its use as a photocatalyst. The energy band structure of a semiconductor is usually an electron-filled low-energy valence band (VB) and an empty high-energy conduction band (CB), and the region between the conduction band and the valence band is called the forbidden band.
When the energy of light irradiating a semiconductor is equal to or greater than the width of the forbidden band, electrons in its valence band are excited, crossing the forbidden band into the conduction band and generating corresponding holes in the valence band. The electrons are excited from the valence band to the conduction band, and some of the separated electrons and holes are further reacted after the excitation.
The photocatalytic reaction mechanism is shown in Fig:

(3) Influencing factors of photocatalytic oxidation process
Studies have shown that the initial concentration of reactants has an obvious influence on the photocatalytic efficiency or degradation rate. The photocatalytic efficiency fluctuates with the increase of the initial concentration, and there is an obvious concentration shift point; the photocatalytic degradation efficiency of the target in low concentration is greater than that of the target in high concentration.
There was no consistent conclusion on the effect of humidity on the photocatalytic reaction. For experimental conditions such as different compounds or different concentrations, there are great differences.
(4) Advantages and disadvantages of the photocatalytic oxidation process
Advantages:
High treatment efficiency, low operating costs, suitable for a wide range of VOCs at low concentrations, especially high removal efficiency for aromatic hydrocarbons;
Disadvantages:
The treatment efficiency of high concentration VOCs is general; it mainly stays in the laboratory stage and lacks practical application.
9, zeolite rotor + RTO process
(1) Process principle:

After passing through the zeolite concentration rotor, the VOCs exhaust gas can be effectively adsorbed in the zeolite to achieve the purpose of removal. The volatile gases adsorbed through the zeolite are cleaned and discharged directly into the atmosphere through the chimney, and the rotor continues to rotate at a speed of 1-6 rpm.
At the same time, the adsorbed volatile organic matter is transferred to the desorption area, where a small stream of heated gas is used to desorb the volatile organic matter, and the desorbed zeolite rotor is rotated to the adsorption area for continuous adsorption of volatile organic gases. After desorption, the concentrated organic waste gas is sent to an incinerator to be burned into carbon dioxide and water vapour for emission into the atmosphere.
2.Technical features





